

研究背景
作为二维材料家族的一员,MXenes具有高机械强度、良好的亲水性、金属导电性和大表面积等优点,与石墨烯相似。由于MXenes的物理和化学特性,它们被认为是具有良好应用前景的压敏材料。例如,MXene的表面含有丰富的功能团,大的比表面积有效地增加了与基材的结合力,使其具有良好的机械性能。金属导电性和间层距使MXenes具有很大的可调电阻范围,这使它们对压力极为敏感。高拉伸性能要求在大压力下有结构上的相互连接的网络,而高灵敏度要求即使在小压力下也有大的结构变形。因此,合理设计传感材料的几何结构对于提高传感器的性能也是非常重要的。最近一维纤维结构和二维平面结构和三维结构已被报道。这些传感器具有高灵敏度、极大的伸展性、良好的灵活性和出色的稳定性,适合在不同的应用场景中进行压力检测。可穿戴式传感器需要穿戴在人体上,所以需要有很好的灵活性,良好的弹性,以及高灵敏度和稳定性。随着研究的不断深入,人们也开始设计各种多功能的传感器,如一体化集成、自供电、自修复、可降解的压力传感器和具有抵抗不同极端环境的传感器。设计和制造可大规模应用的可穿戴传感器需要进一步考虑生产要求,如低生产成本和简单的工艺流程。目前,通过简单的工艺来制备具有优良性能的传感器仍然是一个巨大的挑战。同时实现高灵敏度、宽检测范围、高集成度和多功能性仍然需要广泛的探索。本综述讨论了基于MXene的柔性压阻传感器在制造策略、工作机制和不同应用方面的最新发展。首先,简要介绍了MXene材料的合成、性能和组装方法。然后更详细地讨论了基于MXene的压阻传感器的研究进展和应用。结合基于MXene 的压阻式传感器所开发的各种功能,讨论了多功能化和集成化的趋势。最后,概述了主要的挑战,旨在为未来基于MXenes的压阻式物理传感器的研究提供一个参考。
研究成果
由于MXenes的二维层状结构、高导电性、亲水性和大比表面积,它们已经受到越来越多的关注。由于这些独特的优势,MXenes被认为是柔性压阻传感器应用中非常有竞争力的压力敏感材料。近日,安徽大学物质科学与信息技术研究院量子材料与物理研究所岳阳等人系统综述了MXenes的制备方法、基本性能、组装方法及其在压阻式传感器中的应用进展。还总结了MXene 基压力传感器的多功能集成趋势。最后,描述了基于MXene的压力传感器的机遇和挑战以及MXenes在压力传感器应用领域的巨大前景。
图文导读
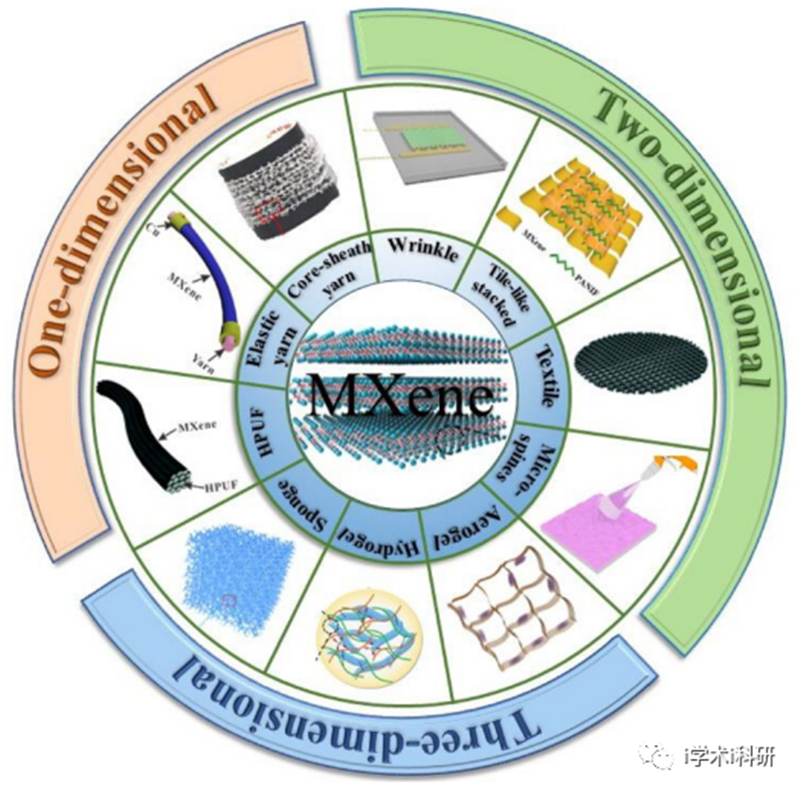
Figure 1. Different structures of MXene-based sensing materials.
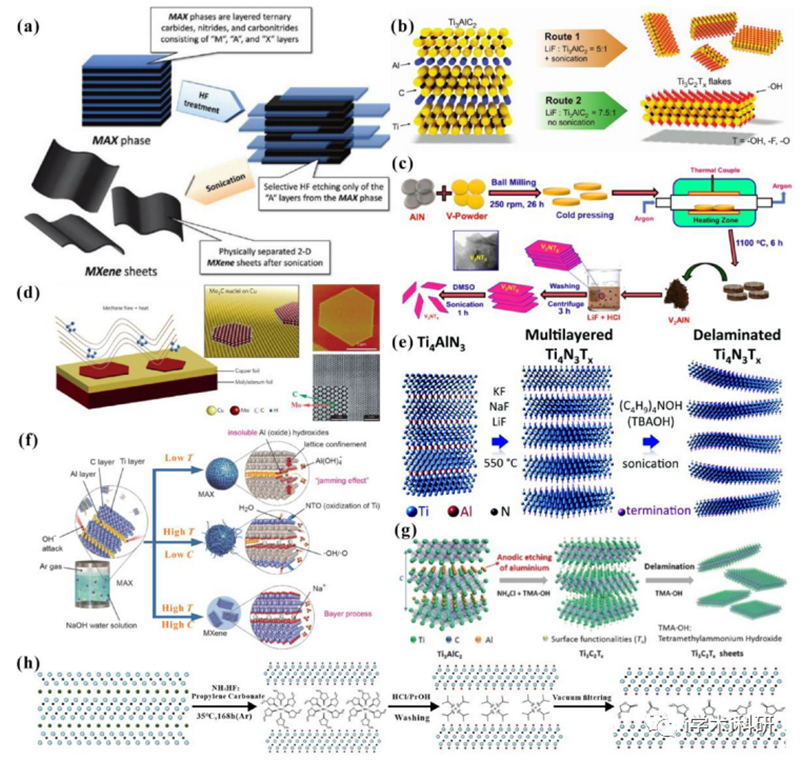
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of MXene synthesis methods.
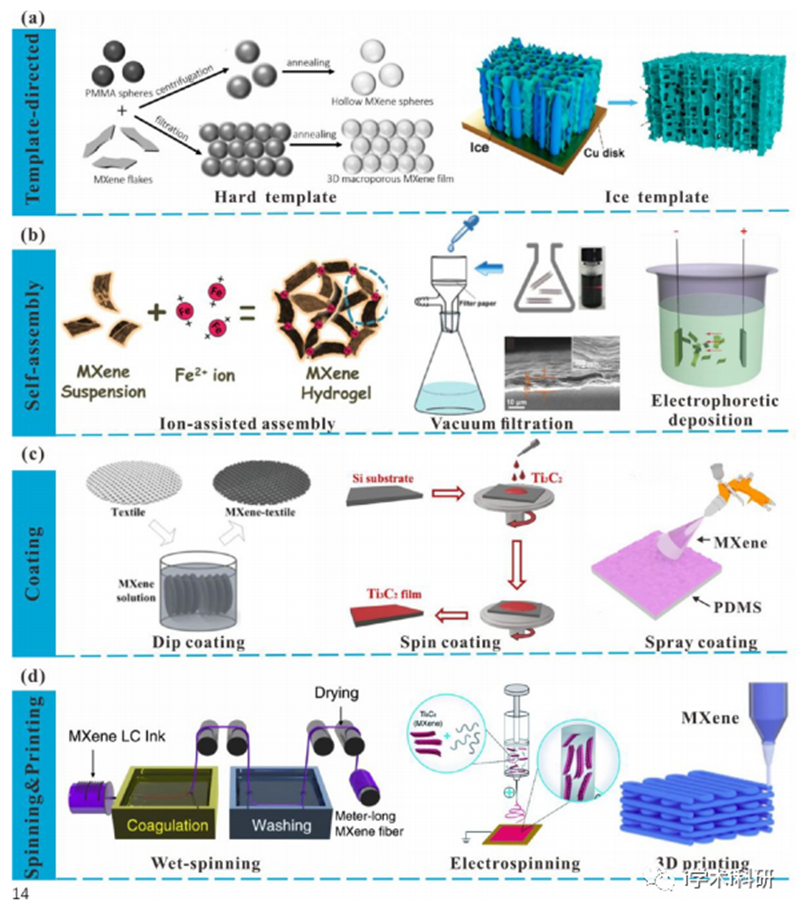
Figure 3. Multiple assembly methods for MXene.
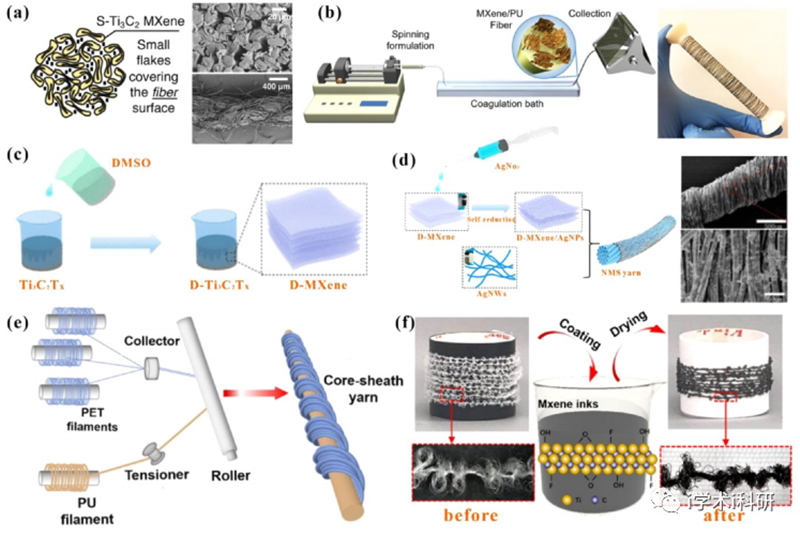
Figure 4. (a) Cross-sectional schematic of cotton yarn coated with MXene flakes and SEM images of the cross-section, surface of the yarn. (b) MXene/PU fiber preparation process by wet spinning. (c) Schematic diagram of MXene nanosheet production process. (d) Preparation process of NMS yarn. (e) Schematic diagram of the core−sheath yarns preparation process. (f) MXene-based core−sheath yarn manufacturing process.
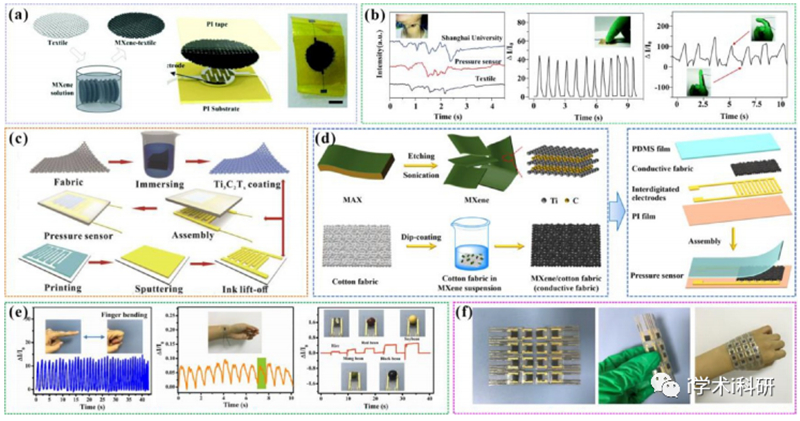
Figure 5. (a) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of MXene textile and sensor. (b) Applications of MXene-textile sensors. (c) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the sensor based on cotton fabric. (d) Schematic illustrations for the fabrication of MCF based pressure sensor. (e) Summary of the pressure sensor performance. (f) Digital photos of e-skin.

Figure 6. (a) Proof-of-concept for MXene-coated cotton human−machine interface (HMI) systems. (b) Photograph of MXene-coated sensing fabric. (c) Schematic illustration of the MXene-coated sensing fabric. (d) Fabrication procedure of MX@SiNP cotton fabric. (e) Fabrication process of Ti3C2Tx−AgNW−PDA/Ni2+ sensor. (f) Fabrication of the Ti3C2Tx/GO strain sensor. (g) Strain sensor based on Ti3C2Tx/G0.5/PDMS structure in different stretching states. (h) Fabrication of the MXene-based sensor with wrinkle structure. (i) Preparation process of viscous Ti3C2Tx@P(VDF-TrFE) N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF)-based suspension and flexible pressure sensor.
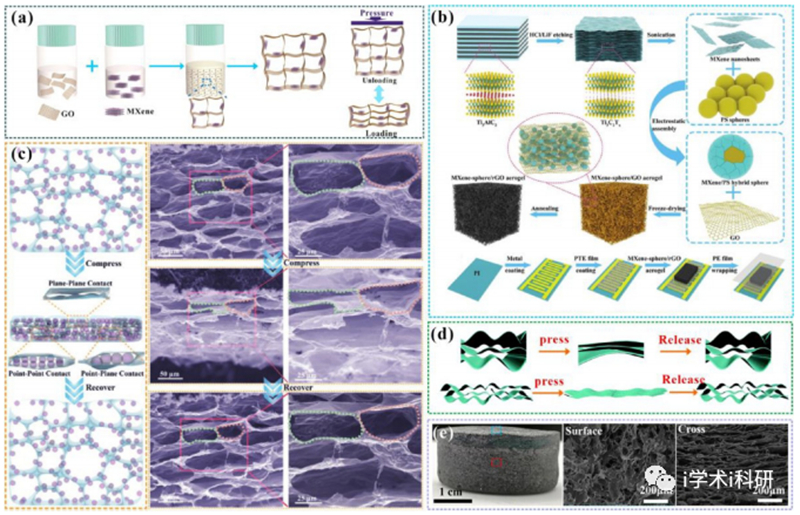
Figure 7. (a) Schematic illustration of the fabrication of MXene/rGO aerogel and sensing mechanism. (b) Fabrication process of MXene-sphere/rGO aerogel and the pressure sensor. (c) Elastic mechanisms and internal microstructures of the pressure sensor. (d) Schematic elasticity mechanisms of C-MX/CNC. (e) Photograph of the MXene/ANF aerogel sensor.

Figure 8. (a) Schematic illustration of MXene-sponge and the piezoresistive sensor. (b) Fabrication procedure of MXene@CS@PU sponge sensor. (c) Photographs of the stretchability and self-healing ability of M-hydrogel. (d) Photographs depicting the low-temperature resistance of MNH and MNOH. (e) Network structure changes during the synthesis of NCDN hydrogel and photographs of the compression sensor. (f) Fabrication of MXene-based pressure sensor with micro-spinous microstructures. (g) Pressure sensor with a microchannel-confined structure. (h) Fabrication process of the sensing material with tile-like stacked hierarchical microstructures.

Figure 9. MXene-based multifunctional sensors.
总结展望
由于MXenes具有二维片状结构、高导电性、大比表面积、亲水性和易于形态控制等特点,它已被广泛应用于储能、吸附、催化和柔性电子设备领域。近年来,各种基于MXenes的可穿戴传感器已经被开发出来。通过在基底材料上涂覆MXene或将其与其他材料复合而制备的普通压阻式和应变式传感器取得了良好的效果,具有各种微结构的MXene基传感器也拓展了传感器的性能。然而,要实现基于MXene材料的传感器的实际大规模实际应用,还有很长的路要走。1) MXene材料的研究,包括性能、制备方法研究、无氟制剂、表面官能团的控制以及成本控制。2) 可穿戴传感器的应用,包括极端环境下性能稳定、传感器监测的准确性、小型化、透气性、防潮湿性等。尽管基于MXene的传感器的大规模应用和商业应用仍存在许多挑战,但不可否认的是,MXene是一种具有巨大潜力的材料,可用于制备高性能传感器,并在未来具有无限的开发潜力。
文献链接
Ti3C2Tx MXene-Based Flexible Piezoresistive Physical Sensors.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c09925.
厦门柔性电子研究院
福建省协同创新院柔性电子产业技术分院
地址:厦门市集美区集美大道1995号科技成果转化加速器1期4F
邮编:361024 电话:0592-5366222 邮箱:admin@flex-elec.com
部分图片来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除