

研究背景
传感器是一种能够将接收到的信息转化为电信号或其他信号输出的检测装置。在这个智能化、数字化、网络化的时代,已经成为获取信息的主要方式和手段。对传感器灵敏度和应用范围的要求也越来越高。传感器的敏感元件对传感器的性能非常重要,它直接影响到传感器的精度、灵敏度和检测范围。本文介绍的传感器在生物医学、柔性压力、光电化学等方面的应用已经渗透到我们生活的各个方面,为现代化的发展做出了无可争议的贡献。
石墨烯是一种单层平面薄膜,具有由碳原子组成的六角形蜂窝状晶格。石墨烯材料因其特殊的结构而具有优良的电气和机械性能,在工程领域引起广泛关注。传感器被认为是石墨烯最有前途的应用之一。目前,已有多种方法可以获得高质量的石墨烯薄膜,如通过化合物对石墨进行化学剥离、在不同基底上进行化学气相沉积(CVD)、 石墨晶体的机械裂解以及其他化学合成方法。其中,化学气相法是一种低成本、高质量、大规模的生产方法,在各个领域发挥着重要作用。由于石墨烯很难用单一原料生产出产品,因此利用石墨烯和其他材料的突出特性形成石墨烯复合材料。石墨烯的大小、层数、形状和化学基团对传感器的性能有很大影响。石墨烯基复合材料可以提高传统传感器的灵敏度和灵活性,缩短反应时间。石墨烯在传感器中的作用毋庸置疑,但如何根据其应用选择合适的石墨烯基材料已成为一个问题。
研究成果
随着石墨烯基材料的研究和发展,基于石墨烯复合材料的新型传感器对科学研究和消费市场具有重要意义。然而,近十年来,由于对传感器精度、可靠性、耐久性的要求,新型石墨烯传感器的发展在未来仍面临诸多挑战。由于石墨烯的特殊结构,获得的特性可以满足高性能传感器的要求。因此,近年来石墨烯材料已被应用于许多创新的传感器材料。东北大学刘纪红教授介绍了近年来基于石墨烯及其基础材料的传感器在生物医学、光电化学、柔性压力等领域的重要作用和具体实例,并提出了石墨烯材料在传感器应用中遇到的困难。最后,对石墨烯传感器的发展方向进行了展望。针对过去两年的COVID-19疫情,对病毒传感器的检测进行了研究。这些新的石墨烯传感器可以在准确度和可靠性的基础上完成信号检测,这为研究人员选择和制造传感器材料提供了参考。相关报道以“Applications of Graphene-Based Materials in Sensors:A Review”为题发表在Micromachines期刊上。
图文导读
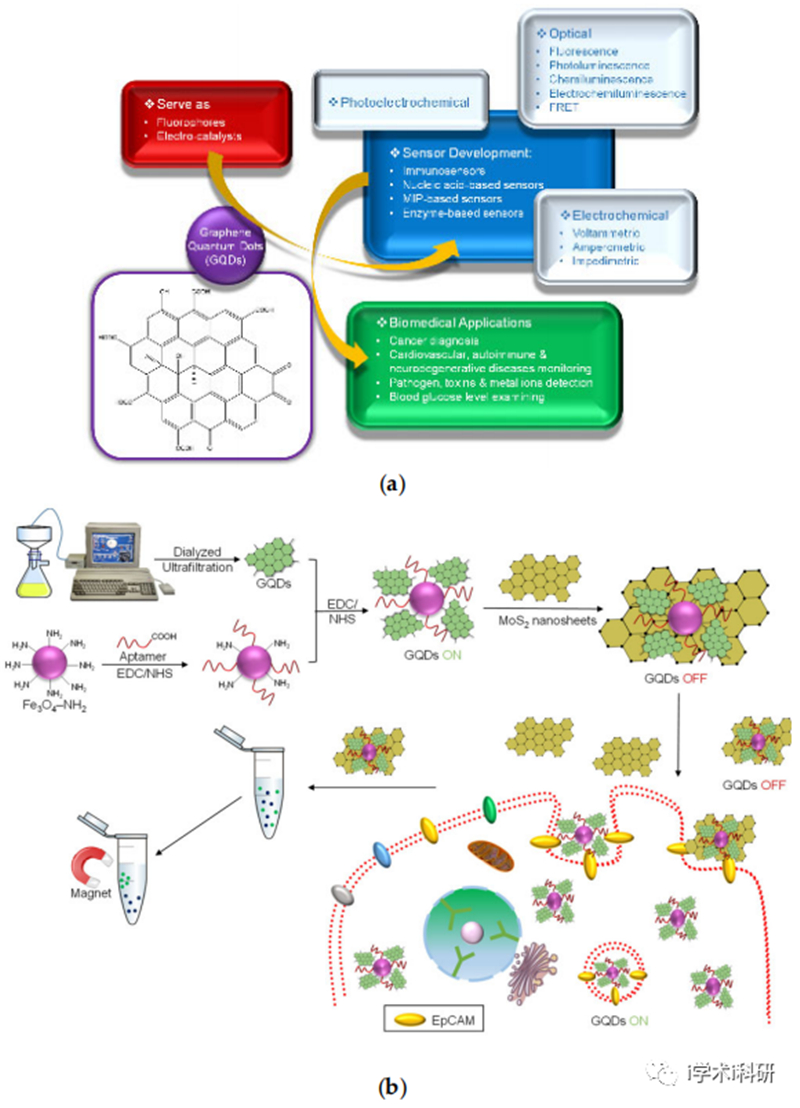
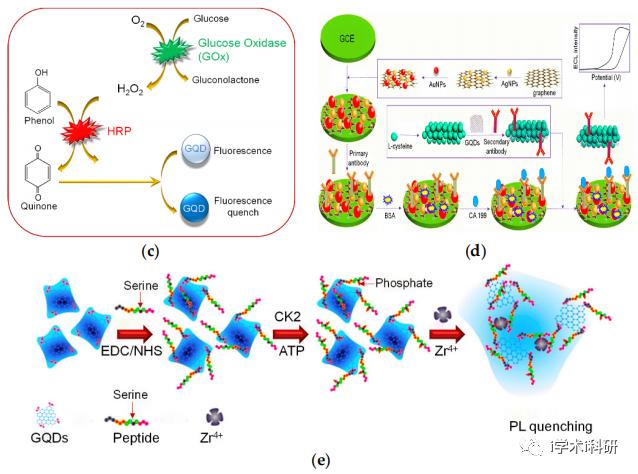
Figure 1. Graphene biosensor. (a) Structure of graphene quantum dots and its application in biomedical sensors; (b) Sensor for detecting tumor cells based on aptamer/Fe3O4/GQDS/MoS2;(c) GQD biosensor based on the synergistic effect of enzyme coupling technology and fluorescence quenching is used to monitor the glucose level in human serum samples;(d) Sensor for detecting carbohydrate antigen in human serum based on GQDs;(e) A GQD sensor based on PL for screening protein kinase activity.
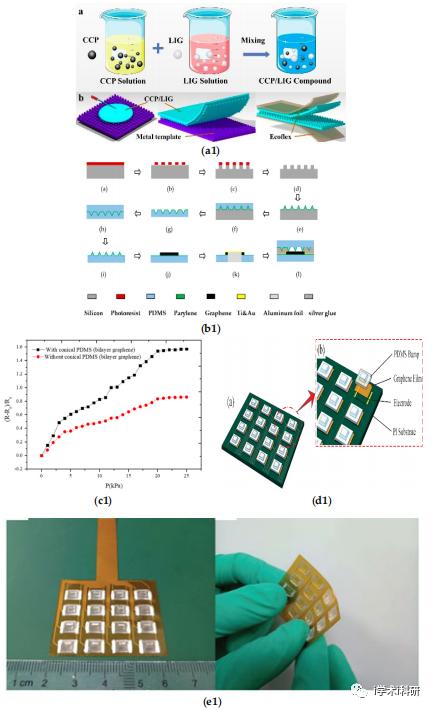
Figure 2. Flexible pressure sensor. (a1) Manufacturing process diagram of LIG/CCG sensor; (b1) Preparation process of a sensor made of conical microstructure PDMS substrate and double-layer graphene; (c1) Sensitivity curve of the sensor with and without conical microstructure; (d1) Structure and enlarged details of electronic skin; (e1) Size and photos of electronic skin.

Figure 3. Photoelectrochemical sensor. (a1) Sensitivity curves of ZnO/graphene sensor under different concentrations of hydrogen; (b1) Reproducibility experiment of ZnO/graphene sensor; (c1) Structure diagram and cross‐section diagram of resonant cavity plasma photon biochemical sensor; (d1) Effect of adjusting Fermi level of graphene on the sensitivity and wavelength of the sensor.
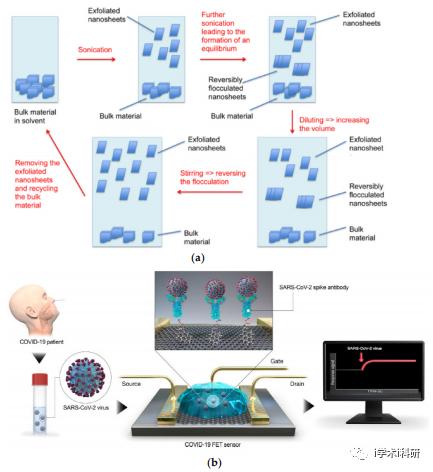
Figure 4. (a) In the improved LPE method, when the sample reaches equilibrium to produce flocculated nanosheets, dilute and stir the sample, remove the exfoliated 2D materials, recover the bulk materials, and repeat the process. (b) 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) field effect transistor (FET)—sensor. Using graphene as sensing material, 1-pyrene butyrate two imide ester (PBASE) was used as an interface molecule and probe connector, and a SARS-CoV-2 peak antibody was used to modify graphene.
总结与展望
本文介绍了石墨烯材料的基本结构信息和特点,阐述了石墨烯材料在生物医学传感器、柔性压力传感器、光电化学传感器等方面的作用,并列举了各领域的应用实例。最后,比较了石墨烯材料的各种制备方法,提出了石墨烯传感器商业化中遇到的困难,并对石墨烯传感器的未来发展提出了一些建议。
文献链接
Applications of Graphene-Based Materials in Sensors: A Review, Micromachines 2022, 13, 184,https://doi.org/10.3390/mi13020184
厦门柔性电子研究院
福建省协同创新院柔性电子产业技术分院
地址:厦门市集美区集美大道1995号科技成果转化加速器1期4F
邮编:361024 电话:0592-5366222 邮箱:admin@flex-elec.com
部分图片来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除